
Watershed
Key Facts
Watershed (noun) an area of land that drains or “sheds” water into a stream or lake.
or
A watershed is like a large bowl collecting water, carrying it downhill and into a stream or lake.
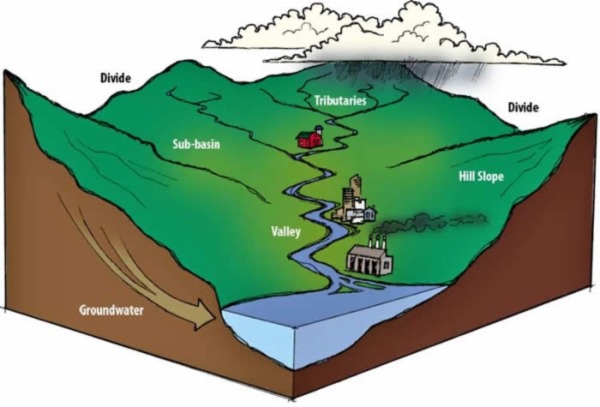
Watch this 1 minute video to learn more about how a watershed works.
- We all live in a watershed.
- All the people who live in a watershed affect the water quality of the water they drink and the water flowing in streams, rivers and lakes in the watershed.
Did You Know?
The Torch Lake Watershed was formed during the ice age 10,000 years ago. Snow accumulated and formed glaciers a mile high. These massive ice sheets advanced and retreated scouring gouges into the granite bedrock. After their last retreat, they left Lake Michigan, the Elk River Chain of Lakes including Torch Lake.
Watershed boundaries do NOT follow township, county, state or country lines.
Michigan contains 65 watersheds and 83 counties.
Our watershed address is:
Great Lakes Basin
– Boardman-Charlevoix Watershed
–Elk River Chain of Lakes Watershed
—Torch Lake Watershed

The Torch Lake Watershed is small. It covers only 76 square miles.
Our watershed is divided into more than 4,500 parcels within its boundary.
Torch Lake is a reflection of its watershed.
Rainwater and snowmelt are called stormwater, which carries soil, nutrients and toxins into more than 40 streams that flow into Torch Lake.
Changing the natural landscape by cutting down trees, building homes and paving driveways, increases the amount of stormwater carrying pollutants into the lake.
Show
You Care
We know you want to enjoy the lake for many years (and generations) to come. So, we’ve put together a list of simple steps you can take to reduce the nutrients, sediments and toxins flowing into the lake and its streams.
The Torch Lake Watershed has high water quality.
Stormwater is one of the greatest threats to Torch Lake.
Keep stormwater on your property:
- Use gravel instead of asphalt for driveways. If your driveway is paved, plant gardens where the water drains instead of emptying into a ditch, stream or directly into Torch Lake.
- Locate the perimeter drain around your home, instead of draining into a ditch, stream or the lake, redirect the pipe into a planted depression or raingarden.
- Restore the natural shoreline by planting trees and plants to trap stormwater.
WATERpedia: the “One-Stop Shop” for Water Science A-Z
A-E
F-M
N-S
T-Z
Don't just wish that Torch Lake will stay blue.
Choose a water-friendly lifestyle - make a difference!
